Australian GDP grew at a robust 3.1% for the year ended 31 March 2018 but a look at the broader economy shows little to cheer about.
Wages growth is slowing, with the Wage Price Index falling sharply.

Falling growth in disposable income is holding back consumption (e.g. retail spending) and increasing pressure on savings.

Housing prices are high despite the recent slow-down, while households remain heavily indebted, with household debt at record levels relative to disposable income.

Housing price growth slowed to near zero and we are likely to soon see house prices shrinking.

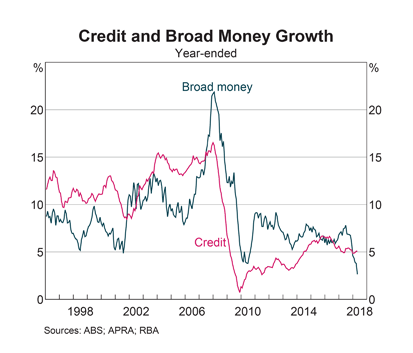
Broad money growth is falling sharply, reflecting tighter financial conditions, while credit growth is also slowing.
Mining profits are up, while non-mining corporation profits (excluding banks and the financial sector) have recovered to about 12% of GDP.

But business investment remains weak, which is likely to impact on future growth in both profits and wages.

Exports are strong, especially in the Resources sector. Manufacturing is the only flat spot.

Iron ore export tonnage continues to grow, while demand for coal has leveled off in recent years.

Our dependence on China as an export market also continues to grow.

Corporate bond spreads — the risk premium over the equivalent Treasury rate charged to non-financial corporate borrowers — remain low, reflecting low financial risk.

Bank capital ratios are rising but don’t be fooled by the risk-weighted percentages. Un-weighted Common Equity Tier 1 leverage ratios are closer to 5% for the four major banks. Common Equity excludes bank hybrids which should not be considered as capital. Conversion of hybrids to common equity was avoided in the recent Italian banking crisis, largely because of the threat this action posed to stability of the entire financial system.

Low capital ratios mean that banks are more likely to act as “an accelerant rather than a shock-absorber” in times of crisis (2014 Murray Inquiry). Professor Anat Admati from Stanford University and Neel Kashkari, President of the Minneapolis Fed are both campaigning for higher bank capital ratios, at 4 to 5 times existing levels, to ensure stability of the financial system. This is unlikely to succeed, considering the political power of the bank sector, unless the tide goes out again and reveals who is swimming naked.
The housing boom has run its course and consumption is slowing. The banks don’t have much in reserve if the housing market crashes — not yet a major risk but one we should not ignore. Exports are keeping us afloat because we hitched our wagon to China. But that comes at a price as Australians are only just beginning to discover. If Chinese exports fail, Australia will need to spend big on infrastructure. And infrastructure that will generate not just short-term jobs but long-term growth.

