Brent crude continued its advance, closing at almost $89 per barrel on Tuesday. Our target is $94 per barrel would increase inflationary pressure in the months ahead and possibly delay Fed rate cuts.

Rising crude oil prices have forced cancellation of plans to restock the strategic petroleum reserve (Bloomberg). US crude and petroleum inventory (including SPR) is testing the lows from January 2023.

Treasury Market
10-Year Treasury yields broke resistance at 4.35% but is retracing to test the new support level. Respect would confirm an advance to test resistance at 5.0%. Failure of support is less likely but would warn of another test of 4.05%.

Federal debt at 120% of GDP, deficits of 6% of GDP, and a growing interest rate burden limit the available options.

The Fed can suppress long-term interest rates but the cost — in terms of inflation — is likely to be high.

The US is well along the path to fiscal dominance as explained in this 2023 paper from the San Francisco Fed:
Fiscal dominance refers to the possibility that the accumulation of government debt and continuing government deficits can produce increases in inflation that “dominate” central bank intentions to keep inflation low….If global real interest rates returned tomorrow to their historical average of roughly 2 percent, given the existing level of US government debt and large continuing projected deficits, the US would likely experience an immediate fiscal dominance problem. Even if interest rates remain substantially below their historical average, if projected deficits occur as predicted, there is a significant possibility of a fiscal dominance problem within the next decade.
The essence of fiscal dominance is the need for the government to fund its deficits on the margin with non-interest-bearing debts. The use of non-interest-bearing debt as a means of funding is also known as “inflation taxation.” Fiscal dominance leads governments to rely on inflation taxation by “printing money” (increasing the supply of non-interest-bearing government debt).
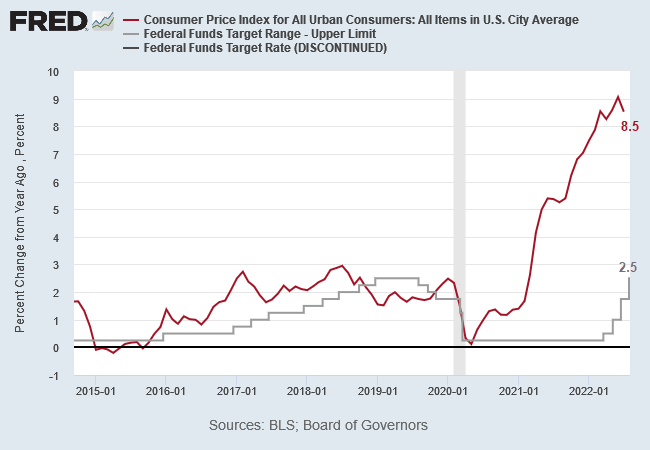
The rise in Gold — currently at $2270 per ounce — reflects bond market fears of an inflation rebound.

The same inflation fears are also driving demand for stocks.

US Economy
The US economy continues to display resilience, with job openings holding steady at 8.8 million in February, exceeding unemployment by a wide margin of 2.3 million.

Light vehicle sales remain robust at a seasonally-adjusted 15.8 million annual rate in February, reflecting consumer confidence.

However, heavy truck sales (41.6K in February) are trending lower — with the 6-month moving average crossing below the 12- month MA — reflecting declining business confidence.

Conclusion
The economy remains robust but fears of an inflation rebound are growing, fueled by rising crude oil prices and large fiscal deficits. The odds of Fed rate cuts in the second half of the year are shrinking but there are still two possible scenarios:
- A sharp decline in economic activity could still prompt the Fed to cut rates despite inflationary fears. That would be a strong bear signal for stocks.
- Fiscal dominance, with the deliberate use of inflation as a tax in order to restore the ratio of debt-to-GDP to more sustainable levels. This involves shrinking the public debt in real terms by expanding GDP through inflation. A strong bull signal for real assets such as Gold, Stocks and Commodities.
Acknowledgements
- EIA, Petroleum & other liquids: Weekly Stocks
- Lyn Alden: Geopolitical Shifts and your Portfolio
- SF Fed, Charles Calomiris: Fiscal Dominance and the Return of Zero-Interest Bank Reserve Requirements