Here is a summary of Colin Twiggs’ presentation to investors at Beech Capital on March 30, 2023. The outlook covers seven themes:
- Elevated risk
- Bank contagion
- Underlying causes of instability
- Interest rates & inflation
- The impact on stocks
- Flight to safety
- Australian perspective
1. Elevated Risk
We focus on three key indicators that warn of elevated risk in financial markets:
Inverted Yield Curve
The chart below plots the difference between 10-year Treasury yields and 3-month T-Bills. The line is mostly positive as 10-year investments are normally expected to pay a higher rate of investment than 3-month bills. Whenever the spread inverted, however, in the last sixty years — normally due to the Fed tightening monetary policy — the NBER has declared a recession within 12 to 18 months1.

The current value of -1.25% is the strongest inversion in more than forty years — since 1981. This squeezes bank net interest margins and is likely to cause a credit contraction as banks avoid risk wherever possible.
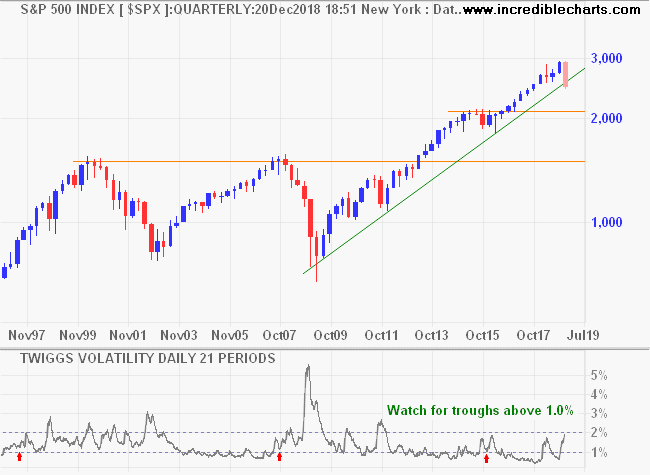
Stock Market Volatility
We find the VIX (CBOE Short-term Implied Volatility on the S&P 500) an unreliable measure of stock market risk and developed our own measure of volatility. Whenever 21-day Twiggs Volatility forms troughs above 1.0% (red arrows below) on the S&P 500, that signals elevated risk.

The only time that we have previously seen repeated troughs above 1.0% was in the lead-up to the global financial crisis in 2007-2008.

Bond Market Volatility
The bond market has a far better track record of anticipating recessions than the stock market. The MOVE index below measures short-term volatility in the Treasury market. Readings above 150 indicate instability and in the past have coincided with crises like the collapse of Long Term Capital Management (LTCM) in 1998, Enron in 2001, Bear Stearns and Lehman in 2008, and the 2020 pandemic. In the past week, the MOVE exceeded 180, its highest reading since the 2008-2009 financial crisis.

2. Bank Contagion
Regional banks in the US had to be rescued by the Fed after a run on Silicon Valley Bank. Depositors attempted to withdraw $129 billion — more than 80% of the bank’s deposits — in the space of two days. There are no longer queues of customers outside a bank, waiting for hours to withdraw their deposits. Nowadays online transfers are a lot faster and can bring down a bank in a single day.
The S&P Composite 1500 Regional Banks Index ($XPBC) plunged to 90 and continues to test support at that level.

Bank borrowings from the Fed and FHLB spiked to $475 billion in a week.

Financial markets are likely to remain unsettled for months to come.
European Banks
European banks are not immune to the contagion, with a large number of banking stocks falling dramatically.

Credit Suisse (CS) was the obvious dead-man-walking, after reporting a loss of CHF 7.3 billion in February 2023, but Deutsche Bank (DB) and others also have a checkered history.

3. Underlying Causes of Instability
The root cause of financial instability is cheap debt. Whenever central banks suppress interest rates below the rate of inflation, the resulting negative real interest rates fuel financial instability.
The chart below plots the Fed funds rate adjusted for inflation (using the Fed’s preferred measure of core PCE), with negative real interest rates highlighted in red.

Unproductive Investment
Negative real interest rates cause misallocation of capital into unproductive investments — intended to profit from inflation rather than generate income streams. The best example of an unproductive investment is gold: it may rise in value due to inflation but generates no income. The same is true of art and other collectibles which generate no income and may in fact incur costs to insure or protect them.
Residential real estate is also widely used as a hedge against inflation. While it may generate some income in the form of net rents, the returns are normally negligible when compared to capital appreciation.
Productive investments, by contrast, normally generate both profits and wages which contribute to GDP. If an investor builds a new plant or buys capital equipment, GDP is enhanced not only by the profits made but also by the wages of everyone employed to operate the plant/equipment. Capital investment also has a multiplier effect. Supplies required to operate the plant, or transport required to distribute the output, are both likely to generate further investment and jobs in other parts of the supply chain.
Cheap debt allows unproductive investment to crowd out productive investment, causing GDP growth to slow. These periods of low growth and high inflation are commonly referred to as stagflation.
Debt-to-GDP
The chart below shows the impact of unproductive investment, with private sector debt growing at a faster rate than GDP (income), almost doubling since 1980. This should be a stable relationship (i.e. a horizontal line) with GDP growing as fast as, if not faster than, debt.

Even more concerning is federal debt. There are two flat sections in the above chart — from 1990 to 2000 and from 2010 to 2020 — when the relationship between private debt and income stabilized after a major recession. That is when government debt spiked upwards.

When the private sector stops borrowing, the government steps in — borrowing and spending in their place — to create a soft landing. Some call this stimulus but we consider it a disaster when unproductive spending drives up the ratio of government debt relative to GDP.
Research by Carmen Reinhart and Ken Rogoff (This Time is Different, 2008) suggests that states where sovereign debt exceeds 100% of GDP (1.0 on the above chart) almost inevitably default. A study by Cristina Checherita and Philip Rother at the ECB posited an even lower sustainable level, of 70% to 80%, above which highly-indebted economies would run into difficulties.
Rising Inflation
Inflationary pressures grow when government deficits are funded from sources outside the private sector. There is no increase in overall spending if the private sector defers spending in order to invest in government bonds. But the situation changes if government deficits are funded by the central bank or external sources.
The chart below shows how the Fed’s balance sheet has expanded over the past two decades, reaching $8.6 trillion at the end of 2022, most of which is invested in Treasuries or mortgage-backed securities (MBS).

Foreign investment in Treasuries also ballooned to $7.3 trillion.

That is just the tip of the iceberg. The US has transformed from the world’s largest creditor (after WWII) to the world’s largest debtor, with a net international investment position of -$16.7 trillion.

4. Interest Rates & Inflation
To keep inflation under control, central bank practice suggests that the Fed should maintain a policy rate at least 1.0% to 2.0% above the rate of inflation. The consequences of failure to do so are best illustrated by the path of inflation under Fed Chairman Arthur Burns in the 1970s. Successive stronger waves of inflation followed after the Fed failed to maintain a positive real funds rate (green circle) on the chart below.

CPI reached almost 15.0% and the Fed under Paul Volcker was forced to hike the funds rate to almost 20.0% to tame inflation.
Possible Outcomes
The Fed was late in hiking interest rates in 2022, sticking to its transitory narrative while inflation surged. CPI is now declining but we are likely to face repeated waves of inflation — as in the 1970s — unless the Fed keeps rates higher for longer.

There are two possible outcomes:
A. Interest Rate Suppression
The Fed caves to political pressure and cuts interest rates. This reduces debt servicing costs for the federal government but negative real interest rates fuel further inflation. Asset prices are likely to rise as are wage demands and consumer prices.
B. Higher for Longer
The Fed withstands political pressure and keeps interest rates higher for longer. This increases debt servicing costs and adds to government deficits. The inevitable recession and accompanying credit contraction cause a sharp fall in asset asset prices — both stocks and real estate — and rising unemployment. Inflation would be expected to fall and wages growth slow. The eventual positive outcome would be more productive investment and real GDP growth.
5. The Impact on Stocks
Stocks have been distorted by low interest rates and QE.
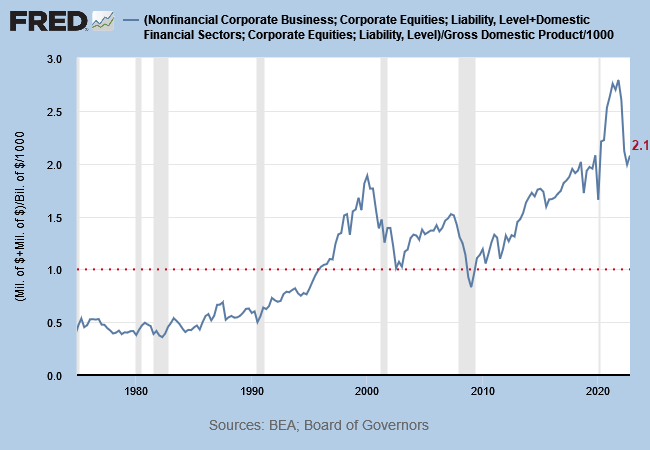
Stock Market Capitalization-to-GDP
Warren Buffett’s favorite indicator of stock market value compares total market capitalization to GDP. Buffett maintains that a value of 1.0 reflects fair value — less than half the current multiple of 2.1 (Q4, 2022).
Price-to-Sales
The S&P 500 demonstrates a more stable relationship against sales than against earnings because this excludes volatile profit margins. Price-to-Sales has climbed to a 31% premium over 20-year average of 1.68.

6. Flight to Safety
Elevated risk is expected to cause a flight to safety in financial markets.
Cash & Treasuries
The most obvious safe haven is cash and term deposits but recent bank contagion has sparked a run on uninsured bank deposits, in favor of short-term Treasuries and money market funds.
Gold
Gold enjoyed a strong rally in recent weeks, testing resistance at $2,000 per ounce. Breakout above $2,050 would offer a target of $2,400.

A surge in central bank gold purchases — to a quarterly rate of more than 400 tonnes — is boosting demand for gold. Buying is expected to continue due to concerns over inflation and geopolitical implications of blocked Russian foreign exchange reserves.

Defensive sectors
Defensive sectors normally include Staples, Health Care, and Utilities. But recent performance on the S&P 500 shows operating margins for Utilities and Health Care are being squeezed. Industrials have held up well, and Staples are improving, but Energy and Financials are likely to disappoint in Q1 of 2023.

Commodities
Commodities show potential because of massive under-investment in Energy and Battery Metals over the past decade. But first we have to negotiate a possible global recession that would be likely to hurt demand.
7. Australian Perspective
Our outlook for Australia is similar to the US, with negative real interest rates and financial markets awash with liquidity.
Team “Transitory”
The RBA is still living in “transitory” land. The chart below compares the RBA cash rate (blue) to trimmed mean inflation (brown) — the RBA’s preferred measure of long-term inflationary pressures. You can seen in 2007/8 that the cash rate peaked at 7.3% compared to the trimmed mean at 4.8% — a positive real interest rate of 2.5%. But since 2013, the real rate was close to zero before falling sharply negative in 2019. The current real rate is -3.3%, based on the current cash rate and the last trimmed mean reading in December.

Private Credit
Unproductive investment caused a huge spike in private credit relative to GDP in the ’80s and ’90s. This should be a stable ratio — a horizontal line rather than a steep slope.

Government Debt
Private credit to GDP (above) stabilized after the 2008 global financial crisis but was replaced by a sharp surge in government debt — to create a soft landing. Money spent was again mostly unproductive, with debt growing at a much faster rate than income.

Liquidity
Money supply (M3) again should reflect a stable (horizontal) relationship, especially at low interest rates. Instead M3 has grown much faster than GDP, signaling that financial markets are awash with liquidity. This makes the task of containing long-term inflation much more difficult unless there is a prolonged recession.

Conclusion
We have shown that risk in financial markets is elevated and the recent bank contagion is likely to leave markets unsettled. Long-term causes of financial instability are cheap debt and unproductive investment, resulting in low GDP growth.
Failure to address rising inflation promptly, with positive real interest rates, is likely to cause recurring waves of inflation. There are only two ways for the Fed and RBA to address this:
High Road
The high road requires holding rates higher for longer, maintaining positive real interest rates for an extended period. Investors are likely to suffer from a resulting credit contraction, with both stocks and real estate falling, but the end result would be restoration of real GDP growth.
Low Road
The low road is more seductive as it involves lower interest rates and erosion of government debt (by rapid growth of GDP in nominal terms). But resulting high inflation is likely to deliver an extended period of low real GDP growth and repeated cycles of higher interest rates as the central bank struggles to contain inflation.
Overpriced assets
Vulnerable asset classes include:
- Growth stocks, trading at high earnings multiples
- Commercial real estate (especially offices) purchased on low yields
- Banks, insurers and pension funds heavily invested in fixed income
- Sectors that make excessive use of leverage to boost returns:
- Private equity
- REITs (some, not all)
Relative Safety
- Cash (insured deposits only)
- Short-term Treasuries
- Gold
- Defensive sectors, especially Staples
- Commodities are more cyclical but there are long-term opportunities in:
- Energy
- Battery metals
Notes
- The Dow fell 25% in 1966 after the yield curve inverted. The NBER declared a recession but later changed their mind and airbrushed it from their records.
Questions
1. Which is the most likely path for the Fed and RBA to follow: the High Road or the Low Road?
Answer: As Churchill once said: “You can always depend on the Americans to do the right thing. But only after they have tried everything else.” With rising inflation, the Fed is running out of options but they may still be tempted to kick the can down the road one last time. It seems like a 50/50 probability at present.
2. Comment on RBA housing?
We make no predictions but the rising ratio of housing assets to disposable income is cause for concern.

3. Is Warren Buffett’s indicator still valid with rising offshore earnings of multinational corporations?
Answer: We plotted stock market capitalization against both GDP and GNP (which includes foreign earnings of US multinationals) and the differences are negligible.