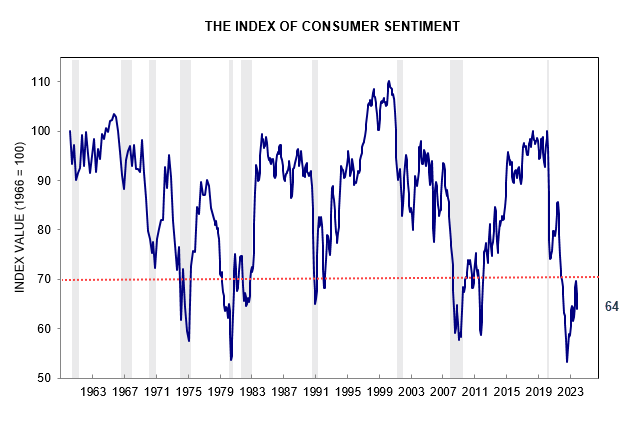
The University of Michigan Index of Consumer Sentiment declined to 61.3 for November. Levels below 70 in the past have signaled a recession.

Consumer sentiment is in sharp contrast to robust personal consumption expenditures which at 93% of disposable personal income are well above pre-pandemic levels.

Mortgage rates above 7.0% failed to dampen discretionary spending, with most households having locked in low fixed mortgage rates over the pandemic.

Home Sales
Existing home sales declined to an annual rate of 3.8 million, with households are reluctant to give up their cheap fixed-rate mortgages.

New home sales surged as a result, boosting residential construction.

Inflation Expectations
The University of Michigan November survey shows 1-year inflation expectations increased to 4.50%.
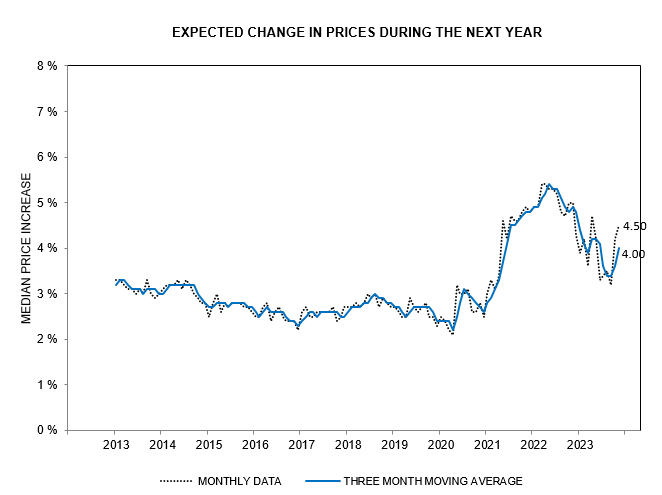
Five-year expectations increased to 3.2%, with the 3-month moving average of 3.0% well above the Fed’s 2.0% target.

Rising inflation expectations mean that the Fed is unlikely to cut interest rates in the foreseeable future.
Interest Rates
10-Year Treasury yields continue to test support at 4.40% after Treasury weighted new issuance towards the front-end of the yield curve — largely funded by money market funds currently invested in repo. Breach of support would offer a target of 4.0% — bearish for the Dollar.

Stocks
The S&P 500 is testing its July high of 4600. Breakout is uncertain but would not signal a bull market unless confirmed by other indices.

The S&P 500 Equal-Weighted Index ($IQX) has recovered less than 60% of its last decline.

The Russell 2000 Small Caps ETF (IWM) is even weaker, retracing less than 50% of its last decline, suggesting that investors have little appetite for risk.

Dow Jones Transportation Average has also retraced less than 50%. The Trend Index below zero continues to warn of selling pressure.

Gold and the Dollar
The Dollar Index retraced to test resistance at 104. Respect is likely and breakout below 103 would offer a target of 100.

The weakening Dollar is bullish for Gold which is testing resistance at $2000 per ounce. Breakout would offer a short-term target of the previous high at $2050.

Commodities
Dow Jones Industrial Metals Index ($BIM) fell sharply, warning of another test of primary support at 153. Breach would warn of a global recession, especially if mirrored by a similar breach in Copper.

Copper is testing its descending trendline at 8300. Reversal below primary support at 7800 would warn of a global recession. China consumes about 50% of the world’s copper production, most of it used in construction. So a lot depends on China’s efforts to rescue their ailing property sector.

The downward spiral of China’s ailing property sector shows no sign of abating despite the government’s rollout of a seemingly endless series of supportive but as yet ineffective measures, with the crisis stretching for over three years…..
The market for Chinese developers’ dollar-denominated bonds has seen a meltdown over the past two years, losing 87% of its value. The rout has wiped out $135.5 billion of value from $154.9 billion of outstanding notes, according to analysis by Debtwire. (Caixin)
Brent crude is testing resistance at $83 per barrel. Respect would warn of another downward leg to $72 and strengthen a bear market warning from Copper and base metals.

Conclusion
Personal consumption expenditures remain strong despite falling consumer sentiment. The S&P 500 is testing resistance at 4600 but the advance is narrow, with investors avoiding risk in the broader market.
The Dollar weakened on the back of falling long-term Treasury yields, boosting demand for Gold which is testing resistance at $2000 per ounce. Breakout would offer a short-term target of $2050.
Copper and base metals are expected to again test primary support as doubts remain over China’s ailing property sector. Breach of support would warn of a global recession.
Inflation expectations remain persistent, with five-year expectations at 3.0% in the November University of Michigan consumer survey, well above the Fed’s target of 2.0%. The likelihood of rate cuts in early 2024 is remote unless a major collapse in financial markets forces the Fed’s hand.
Acknowledgements
Macrobusiness: China’s property black hole sucks in the CCP.