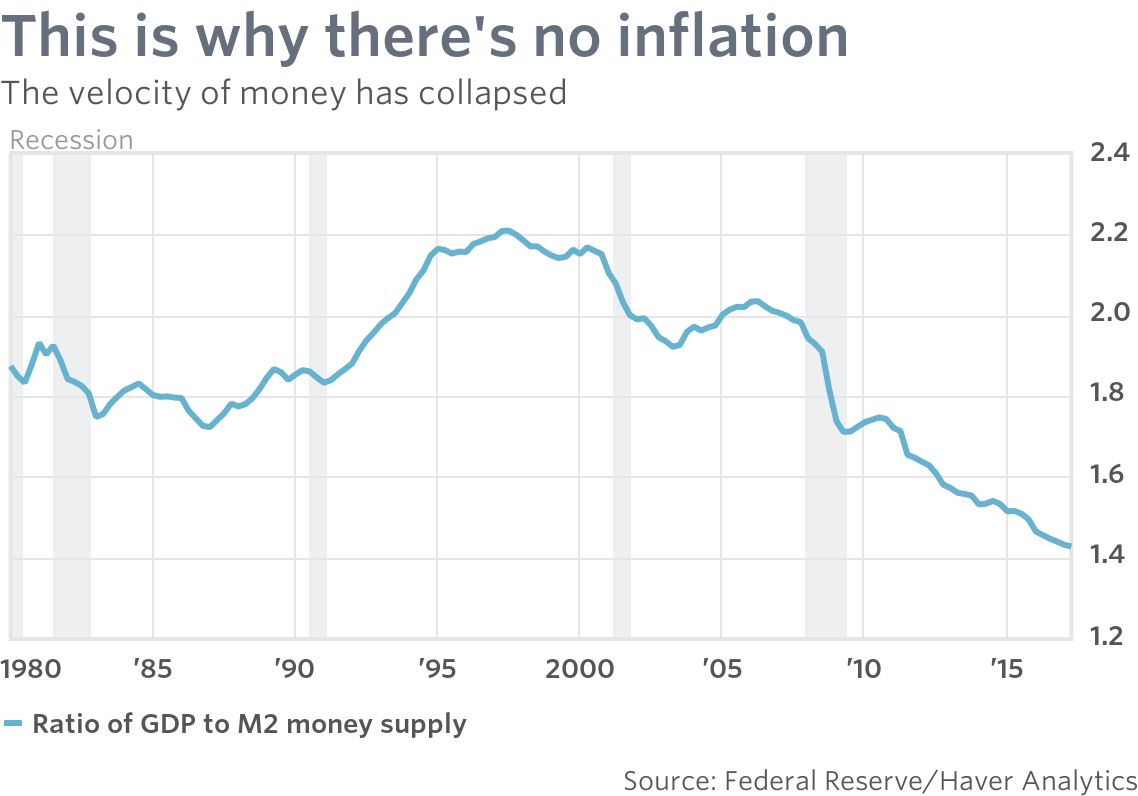
Some writers have attributed slow GDP growth in the US to the plunging velocity of money.
In layman’s terms, the velocity of money is the ratio between your bank balance and the amount you spend. For the economy as a whole, it is measured as the ratio of GDP (or national income) against the total stock of money (or money supply).
When the economy is hot, consumers have a higher propensity to spend — or invest in the latest hot stock — and the ratio normally rises. When the economy cools, the ratio falls.
If the ratio was fixed, the job of central bankers would be simple: print more money and GDP would rise.

Unfortunately that is not the case. GDP growth has remained slow, post-2007, despite a sharp boost in the money supply.
M1 is a narrow definition of money: cash in circulation plus travelers checks, demand deposits (at call) and check account balances.
The ratio of GDP to M1 money (or M1 Velocity) has almost halved, from a 2007 high of 10.7 to a current low of 5.5.

Does this mean that consumers are feverishly stuffing cash into mattresses as the economy goes into a death-dive or is there a more rational explanation?
Examine the above chart more closely and you will see a clear relationship until 1980 between the velocity of money and interest rates (in this case the Fed funds rate). When interest rates rise, the velocity of money rises. So when interest rates fall, as they have post-2007, to near zero, the velocity of money should fall. As it has done.
The anomaly is not the current fall in the velocity of money but the rise in velocity of money between 1990 and 2000, when interest rates were falling. There are two explanations that I can think of. One is the digital revolution, with the advent of online bank accounts and automated clearing of business checking accounts which enabled depositors to minimize balances in non-interest bearing accounts. Second, is the rapid growth of money market funds which fall outside the ambit of M1 and M2.
Velocity of money measured as GDP/MZM gives a clearer picture, with velocity rising when rates rise and falling when rates fall. MZM is M1 plus all savings deposits and money market funds that are redeemable (at par) on demand.

We should expect to see the velocity of money recover as interest rates rise. If that doesn’t happen, then it will be time to worry.
Strange as it may seem, we could witness something really unusual: if higher interest rates stimulate GDP.

Colin Twiggs is a former investment banker with almost 40 years of experience in financial markets. He co-founded Incredible Charts and writes the popular Trading Diary and Patient Investor newsletters.
Using a top-down approach, Colin identifies key macro trends in the global economy before evaluating selected opportunities using a combination of fundamental and technical analysis.
Focusing on interest rates and financial market liquidity as primary drivers of the economic cycle, he warned of the 2008/2009 and 2020 bear markets well ahead of actual events.
He founded PVT Capital (AFSL No. 546090) in May 2023, which offers investment strategy and advice to wholesale clients.