Seasonally adjusted labour force estimates show a decline in October 2019:
- Employment decreased by 19,000 to 12,919,200 people
(full-time -10,300 and part-time -8,700).
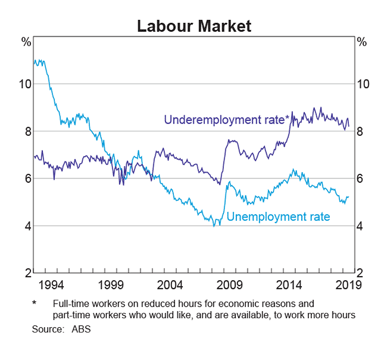
- Unemployment rate increased by 0.1 pts to 5.3%.
- Monthly hours worked in all jobs decreased by 2.8 million hours to 1,783.9 million hours.
The leading indicator of employment has been predicting a down-turn in employment for some time, recording its sixteenth consecutive monthly fall in November.

Job advertisements have also declined since late 2018.

Falling employment has a knock-on effect in other areas of the economy:
According to Tony Weber, chief executive of the FCAI, new vehicles have now seen the nineteenth consecutive month of decreasing sales in the Australian market, with October 2019 sales down 9.1% compared to October 2018.
“Year to date sales of new motor vehicles in 2019 are almost 78,000 units (eight per cent) lower than the same period in 2018…”
Retail sales are also soft:
In volume terms, the seasonally adjusted estimate for the September quarter 2019 fell 0.1%. This follows a 0.1% rise in the June quarter 2019, and a 0.1% fall in the March quarter 2019.
But the ASX 200, seemingly unperturbed, is testing resistance at 6800. Breakout would signal a primary advance with a target of 7200. Breach of support at 6400 seems unlikely but would warn of a decline with a target of 5400.

There are, however, signs of weakness in the largest two sectors.
ASX 300 Banks index penetrated its rising trendline, warning of a correction. Declining peaks on the Trend Index indicate secondary selling pressure. Follow-through of the index below 7600 would strengthen the bear signal.

A hanging man candlestick warns the ASX 300 Metals & Mining index is likely to again test support at 4100 ( the neckline of a large head-and-shoulders reversal pattern ). A Trend Index peak near zero would indicate continued selling pressure.

Iron ore continues its primary decline, since breaking support at 90. Our long-term target is 65.

We maintain low exposure to Australian equities, with a focus on defensive and contra-cyclical stocks, because of our bearish outlook. But ASX 200 breakout above 6800 would force us to re-examine our outlook.









































You must be logged in to post a comment.