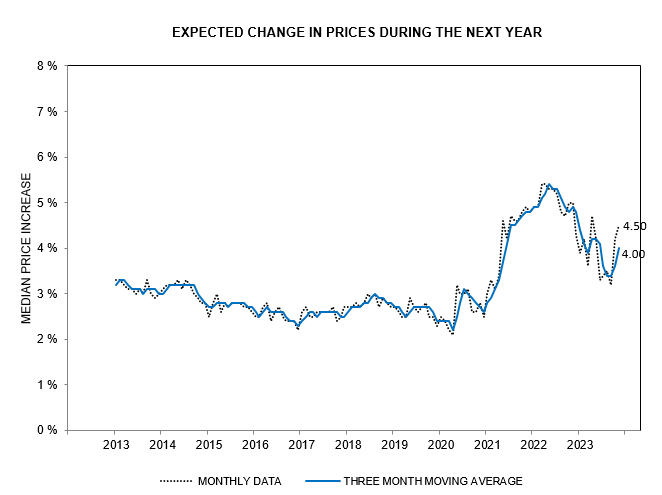
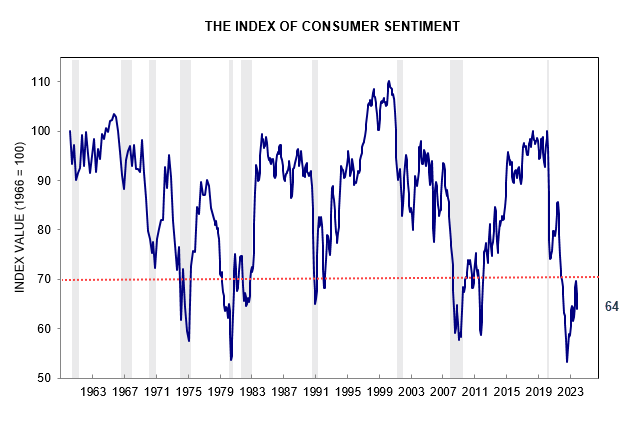
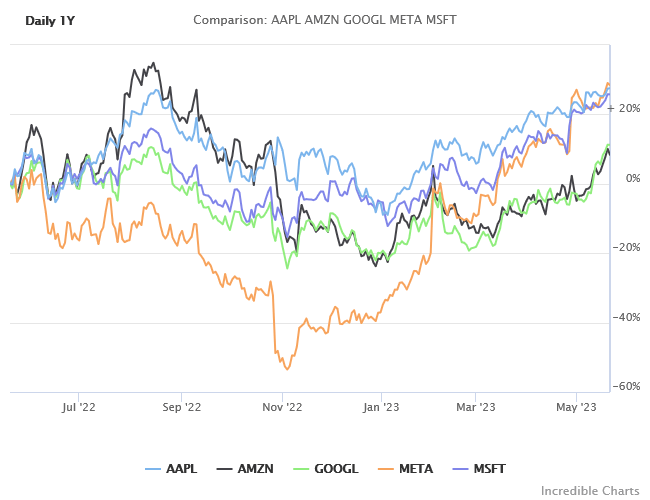
China’s economy is struggling despite injection of moderate stimulus and efforts to support a collapsing real estate sector. Shrinking demand from China threatens a global economic contraction. G7 central banks have responded with monetary easing, causing a broad rally in stocks. This is most likely a bear market rally, with far shorter duration than a bull market.
China’s Shanghai Composite Index is testing primary support at 2900, warning of an economic contraction. The Trend Index peak near zero confirms selling pressure.

Copper, however, has penetrated its descending trendline. Follow-through above 8500 would test resistance at $8750 per metric ton, threatening a wide double-bottom reversal with a target of $9500. Breakout above $8750 would signal global economic recovery, while reversal below $7800 would warn of a global recession.

US Stocks
The S&P 500 is testing it 2022 high at 4800, buoyed by injections of liquidity into financial markets.

The equal-weighted S&P 500 broke resistance at 6300, suggesting a broader rally than just the top 7 stocks. Retracement that respects the new support level would confirm the target at 6665.

The Russell 2000 small caps ETF (IWM) threatens a similar breakout above 200, offering a target of 240. Breakout would confirm that investors are growing more aggressive (risk-on) and downplaying risks.

Interest Rates
Ten-year Treasury yields are retracing to test resistance at 3.9% or 4.0%; respect is likely and would confirm the target of 3.5%.

An increase in supply of Treasury Notes will test bulls’ conviction next week:
A raft of fresh, post-Christmas government bond supply will put that comprehensive bullishness to the test. Next week, Treasury will auction $57 billion, $58 billion and $40 billion in two-, five- and seven-year notes, respectively. That’s up 20%, 15% and 7% from their average sizes over the past four monthly auctions. (Grant’s Current Yield)
The 2-year Treasury yield (purple below) is falling in anticipation of Fed rate cuts next year. A peak in the 2-year tends to lead the first rate cuts by 6 to 9 months. The signal misfired with the SVB banks crisis in March but the October peak warns of Fed rate cuts in Q2 or Q3 of 2024.

International Stocks
The FTSE 100 is testing resistance at 7700, with a Trend Index trough at zero signaling buying pressure.

The DJ Stoxx Euro 600 — reflecting the top 600 stocks in Europe — broke resistance at 470. Follow-through above 480 would test the 2022 high of 494.

Japan’s Nikkei 225 is testing long-term resistance at 33750. Breakout would signal a fresh primary advance but declining Trend Index peaks show a lack of commitment from buyers.

The ASX 200 is testing resistance at 7600, buoyed by strong iron ore prices and falling long-term bond yields. A sharp rise in the Trend Index indicates buying pressure but reversal below 7400 would warn of a correction to test support at 7000.

Gold & the Dollar
The US Dollar Index respected resistance at 102.50, confirming the target at 100. Trend Index peaks below zero signal strong selling pressure.

Gold broke through resistance at $2050, closing at $2053 per ounce. Expect retracement to test the new support level; respect would confirm another attempt at $2100. A falling Dollar and increased bullion demand from central banks is expected to maintain upward pressure on Gold prices.

Conclusion
Stocks are rallying in response to falling long-term Treasury yields and in anticipation of Fed rate cuts next year. But falling LT Treasury yields is a medium-term rally in a long-term bear market, with LT yields expected to rise in 2025. Fed rate cuts are also a bearish sign, normally preceding a recession by several quarters — falling earnings are definitely not bullish for stocks.
Investors will need to be agile, to take advantage of the current bullishness in stocks while guarding against:
- a trend reversal in long-term yields; and
- signs that the broad economy is falling into recession.
Vacation
This is our last newsletter of the year as we close our office for two weeks over Christmas and the New Year.
We wish all our readers peace and goodwill over the festive season and hope for a less tumultuous year ahead.

The Magpie by Claude Monet