From Dr Lacy Hunt at Hoisington Investment Management on the declining velocity of money:

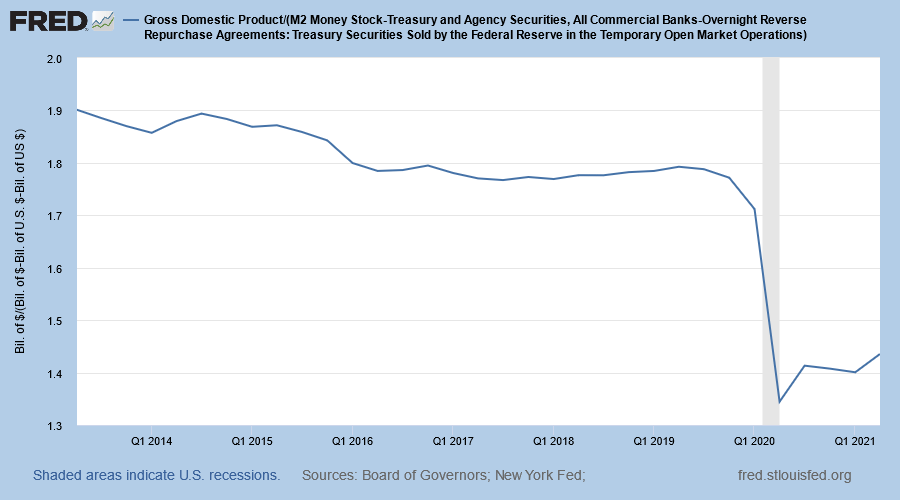
The Fed is able to increase money supply growth but the ongoing decline in velocity (V) means that the new liquidity is trapped in the financial markets rather than advancing the standard of living by moving into the real economy…..

Money and debt are created simultaneously. If the debt produces a sustaining income stream to repay principal and interest, then velocity will rise since GDP will eventually increase beyond the initial borrowing. If advancing debt produces increasingly smaller gains in GDP, then V falls. Debt financed private and governmental projects may temporarily boost GDP and velocity over short timespans, but if the projects do not generate new funds to meet longer term debt servicing obligations, then velocity falls as the historical statistics confirm.
The increase in M2 is not channeled into productive investment — that fuels GDP growth — but rather into unproductive investment in financial assets. The wealthy invest in real assets, as a hedge against inflation, but these are mainly speculative assets — such as gold, precious metals, jewellery, artworks and other collectibles, high-end real estate, or cryptocurrencies — which seldom produce much in the way of real income, with the speculator relying on asset price inflation and low interest rates to make a profit. Many so-called “growth stocks” — with negative earnings — fall in the same category. Debt used to fund stock buybacks also falls in this category as their purpose is financial engineering, with no increase in real earnings.
In 2008 and 2009 Carmen Reinhart and Ken Rogoff (R&R) published research that indicated from an extensive quantitative analysis of highly indebted economies that their economic growth was significantly diminished once they become highly over-indebted.
…..Cristina Checherita and Philip Rother, in research for the European Central Bank (ECB) published in 2014, investigated the average effect of government debt on per capita GDP growth in twelve Euro Area countries over a period of about four decades beginning in 1970. Dr. Checherita, now head of the fiscal affairs division of the ECB and Dr. Rother, chief economist of the European Economic Community, found that a government debt to GDP ratio above the turning point of 90-100% has a “deleterious” impact on long-term growth. In addition, they find that there is a non-linear impact of debt on growth beyond this turning point. A non-linear relationship means that as the government debt rises to higher and higher levels, the adverse growth consequences accelerate……Moreover, confidence intervals for the debt turning point suggest that the negative growth rate effect of high debt may start from levels of around 70-80% of GDP.
…..Unfortunately, early-stage economic expansions do not fare well when inflation and interest rates are not declining at this stage of the business cycle, which is not the normal historical role, or the path indicated by economic theory. As this year has once again confirmed, in early expansion inflationary episodes, prices rise faster than real wages, thereby stunting consumer spending. The faster inflation also thwarts the needed continuing cyclical decline in money and bond yields, which are necessary to gain economic momentum.
…..The U.S. economy has clearly experienced an unprecedented set of supply side disruptions, which serve to shift the upward sloping aggregate supply curve inward. In a graph, with aggregate prices on the vertical axis and real GDP on the horizontal axis, this causes the aggregate supply and demand curves to intersect at a higher price level and lower level of real GDP. This drop in real GDP, often referred to as a supply side recession, increases what is known as the deflationary gap, which means that the level of real GDP falls further from the level of potential GDP. This deflationary gap in turn leads to demand destruction setting in motion a process that will eventually reverse the rise in inflation.
Currently, however, the decline in money growth and velocity indicate that the inflation induced supply side shocks will eventually be reversed. In this environment, Treasury bond yields could temporarily be pushed higher in response to inflation. These sporadic moves will not be maintained. The trend in longer yields remains downward.
Negative real yields
A negative real yield points to the fact that investors or entrepreneurs cannot earn a real return sufficient to cover risks. Accordingly, the funds for physical investment will fall and productivity gains will erode which undermines growth. Attempting to counter this fact, central banks expand liquidity but the inability of firms to profitably invest causes the velocity of money to fall but the additional liquidity boosts financial assets. Financial investment, however, does not raise the standard of living. While the timing is uncertain, real forward financial asset returns must eventually move into alignment with the already present negative long-term real Treasury interest rates. This implied reduction in future investment will impair economic growth.
….research has documented that extremely high levels of governmental indebtedness suppress real per capita GDP. In the distant past, debt financed government spending may have been preceded by stronger sustained economic performance, but that is no longer the case. When governments accelerate debt over a certain level to improve faltering economic conditions, it actually slows economic activity. While governmental action may be required for political reasons, governments would be better off to admit that traditional tools would only serve to compound existing problems.
Carmen Reinhart, Vincent Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff (which will be referred to as RR&R), in the Summer 2012 issue of the Journal of Economic Perspectives linked extreme sustained over indebtedness with the level of interest rates…… “Contrary to popular perception, we find that in 11 of the 16 debt overhang cases, real interest rates were either lower or about the same as during the lower debt/GDP years. Those waiting for financial markets to send the warning signal through higher (real) interest rates that governmental policy will be detrimental to economic performance may be waiting a long time.”
Growth Obstacles
In 2022, several headwinds will weigh on the U.S. economy. These include negative real interest rates combined with a massive debt overhang, poor domestic and global demographics, and a foreign sector that will drain growth from the domestic economy. The EM and AD (Advanced) economies will both serve to be a restraint on U.S. growth this year and perhaps significantly longer. The negative real interest rates signal that capital is being destroyed and with it the incentive to plough funds into physical investment.
Demographics continue to stagnate in the United States and throughout the world……..Poor demographics retard economic growth by lowering household, business and state and local investment. This keeps intact the observable trend in numerous countries – extreme over-indebtedness reduces economic growth which, in turn, worsens demographics, which reinforces the weakness emanating from the debt overhang. William Stull, Professor of Economics at Temple University, makes the case that for nations’, “demographics is destiny” (a phrase coined by Ben Wattenberg and Richard M. Scammon), highlighting the importance of its critical secular growth in determining economic fortune.
Although fourth quarter numbers are not yet available, the global debt to GDP average for 2020-21 is almost certainly the highest on record for any two-year period. Transitory growth spurts, like the one Q4 2021, are unlikely to be sustained. The sporadic but weakening growth trend evident before the pandemic hit in 2019 will return, reinforcing the debt trap.
Inflation
The University of Michigan indicates consumer sentiment in the fourth quarter was worse than during the height of the 2020 pandemic and at the levels of the beginning of the very deep 2008-09 recession. Consumers cut back significantly on their buying plans as expectations for increases in future income slumped. To fund the sharply higher cost of necessities, households have been forced to reduce the personal saving rate in November to 6.9%, or 0.4% less than in December 2019. Needing to tap credit card lines undoubtedly contributed to the erosion in consumer confidence measures. Without the sizable cut in personal saving, real consumer expenditures were barely positive in the fourth quarter. With money growth likely to slow even more sharply in response to tapering by the FOMC, the velocity of money in a major downward trend, coupled with increased global over-indebtedness, poor demographics and other headwinds at work, the faster observed inflation of last year should unwind noticeably in 2022.
























 Click to play
Click to play