Bob Doll from Nuveen Investments is more bullish on stocks than I am but sets out his thoughts on what could cause the current run to end:
“Stock valuations are starting to look full, and technical factors are beginning to appear stretched. As stock prices have risen since last summer, bond yields have crept higher. Should this trend persist, it could eventually cause a headwind for stocks. Credit spreads are signaling some risks, as non-energy high yield corporate bond spreads have dropped to multi-decade lows.
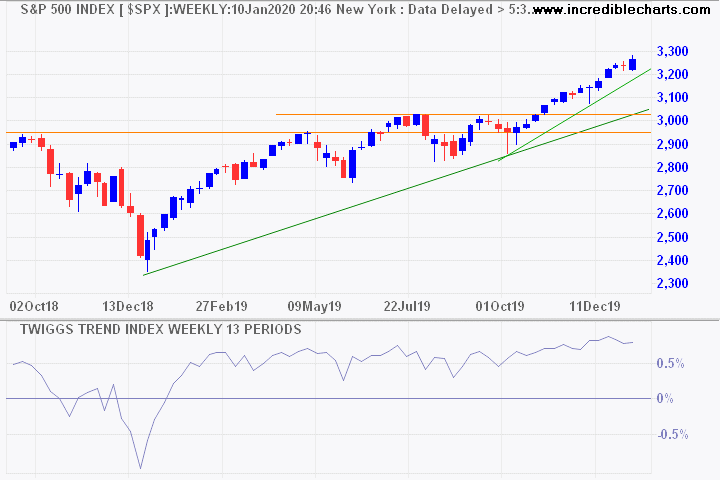
As such, we think stocks may be due for a near-term correction or consolidation phase. Nevertheless, we expect any such phase to be mild and brief as long as monetary conditions remain accommodative and economic and earnings growth holds up. In other words, although we see some near-term risks, we don’t think this current bull market is ending.
That raises the question of what might eventually cause the current cycle to end. We see three possibilities. First, recession prospects could increase significantly. We see little chance of that happening any time soon, given solid economic fundamentals. Second, a political disruption like a resurgence in trade protectionism could occur. We also don’t think that is likely to happen, especially in an election year. Third, bond yields and interest rates could move higher as economic conditions improve, creating problems for stocks. This one seems like a higher probability, and we’ll keep an eye on it.”
Economy
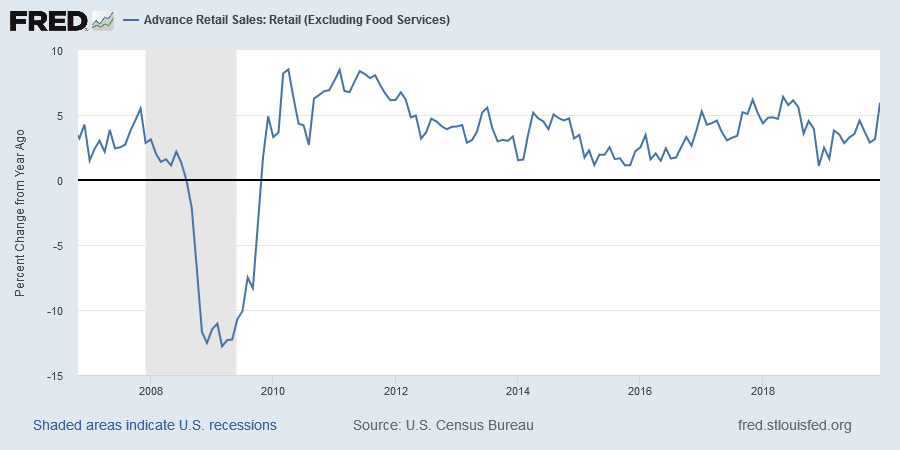
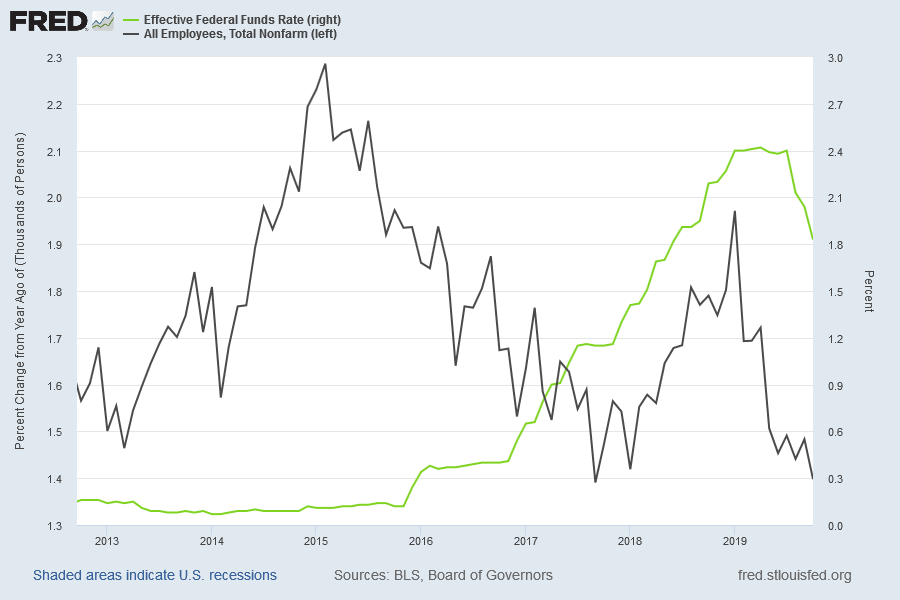
The upsurge in retail sales and housing starts may have strengthened Bob’s view of the economy but manufacturing is in a slump and slowing employment growth could hurt consumption. The inverted yield curve is a long-term indicator and I don’t yet see any indicators confirming an imminent collapse.

I rate economic risk as medium at present.
Political Disruption
US-China trade risks have eased but I continue to rate political disruption as a risk. This could come from any of a number of sources. US-Iran is not over, the Iranians are simply biding their time. Putin’s attempted constitutional coup in Russia. China-Taiwan. Libya. North Korea. Brexit is not yet over. Huawei and 5G are likely to disrupt relations between China, the US and European allies, with China threatening German automakers. Europe also continues to wrestle with fallout from the euro monetary union, a system that is likely to eventually fail despite widespread political support. Impeachment of Trump may not succeed because of the Republican majority in the senate but could produce even more erratic behavior with an eye on the upcoming election. Who can we bomb next to win more votes?
Bonds & Interest Rates
I don’t see inflation as a major threat — oil prices are low and wages growth is slowing — and the Fed is unlikely to raise interest rates ahead of the November election. Bond yields may rise if China buys less Treasuries, allowing the Yuan to strengthen against the Dollar, but the Fed is likely to plug any hole in demand by further expanding its balance sheet.
Market Risk: Irrational Exuberance
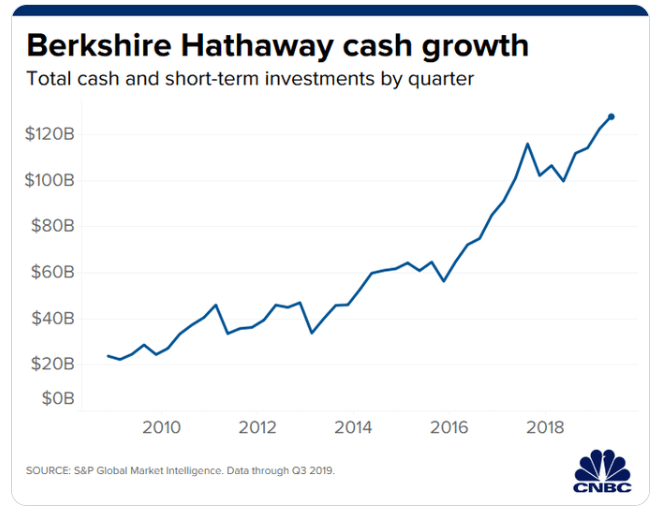
The market is running on more stimulants than a Russian weight-lifter. Unemployment is near record lows but Treasury is still running trillion dollar deficits.

While the Fed is cutting interest rates.

And again expanding its balance sheet. More than twelve years after the GFC. The blue line reflects total assets on the Fed’s balance sheet, mainly Treasuries and MBS, while the orange line (right-hand scale) shows how shrinking excess reserves on deposit at the Fed have helped to create a $2 trillion surge in liquidity in financial markets since 2009. Even when the Fed was supposedly tightening, with a shrinking balance sheet, in 2018 to 2019.

The triple boost has lifted stock valuations to precarious highs. The chart below compares stock market capitalization to profits after tax over the past 60 years.

Ratios above 15 flag that stocks are over-priced and likely to correct. Peaks in 1987 and 2007, shortly before the GFC, are typical of an over-heated market. The Dotcom bubble reflected “irrational exuberance” — a phrase coined by then Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan — and I believe we are entering a second such era.
Recovery of the economy under President Trump is no economic miracle, it is simply the triumph of monetary and fiscal stimulus over rational judgement. Trump knows that he has to keep the party going until November to win the upcoming election, so expect further excess. Whether he succeeds or not is unsure but one thing is certain: the longer the party goes on, the bigger the hangover.
William McChesney Martin Jr., the longest-serving Fed Chairman (1951 to 1970), famously described the role of the Fed as “to take away the punch bowl just as the party gets going.” Unfortunately Jerome Powell seems to have been sufficiently cowed by Trump’s threats (to replace him) and failed to follow that precedent. We are all likely to suffer the consequences.