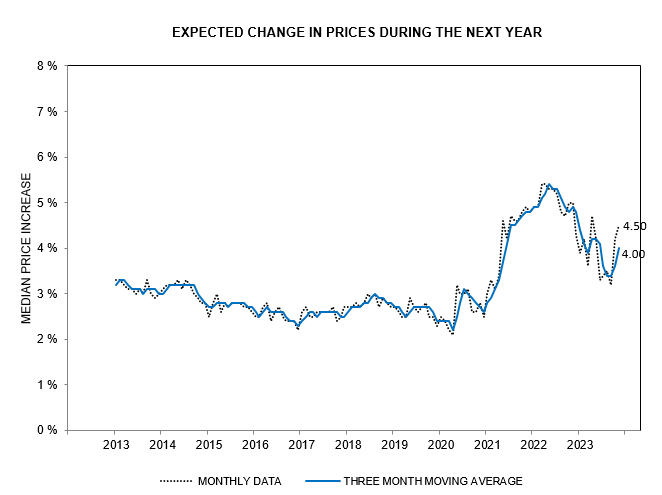
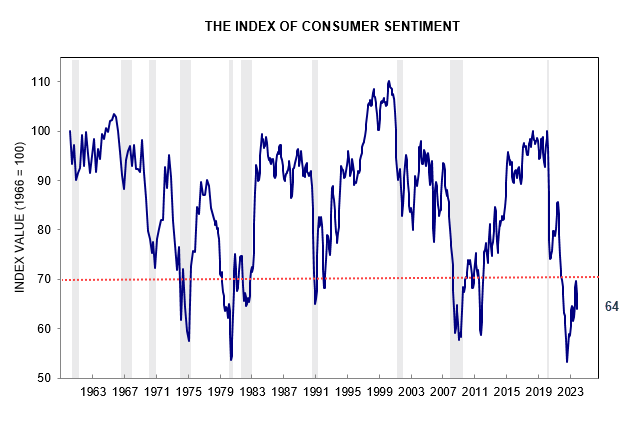
What economic path are the US and major allies likely to take over the next decade? Here is my take on how this is likely to pan out.
First, let’s start with a template of what a healthy, growing economy looks like.
A Virtuous Cycle
Growth is dependent on two factors:
- Demographics — that is a growing, skilled workforce; and
- Productivity — where output grows at a faster rate than the workforce.
Growth requires not only a growing population but a growing workforce. An ageing population or large population under the age of 25 is unlikely to contribute much to output. What is needed are people of 25 to 55 who hold down productive jobs. We also need to ensure that they have the necessary skills — productivity tends to rise with education levels. Education that is skills-based is worth a lot more than a barista with a bachelors degree.
The most important source of productivity growth, however, is investment. More specifically, private investment — government investment tends to provide a short-term boost to the economy but acts as a long-term drag on growth (Dr Lacy Hunt). Mechanization and automation increase the output per worker, boosting productivity.
The chart below shows US private domestic non-residential investment (blue) at a healthy 13.5% of GDP, while productivity (magenta), calculated as real GDP/total non-farm employees, has grown steadily since the 1950s.

Savings are needed to fund private investment. Either domestic savings or offshore borrowings. Domestic savings are better than foreign debt, especially if debt is denominated in a second currency which can cause volatile short-term capital flows. Workers tend to consume what they earn, with low rates of savings, while the wealthy tend to have far higher savings rates. High levels of inequality increases the amount of saving but depresses consumption. Low consumption leads to fewer investment opportunities, so it is important to get the balance right. Forcing workers to save (e.g. through compulsory superannuation) is one solution.
Low deficits are essential to ensure that government borrowing does not crowd out private investment. Government investment — as we mentioned earlier — is no substitute for private investment as it leads to low productivity and low growth.
Monetary policy is often used to prime the pump — stimulating consumption and investment through low interest rates. But cheap debt has short-term benefits and long-term costs that are often not carefully considered. First, low interest rates discourage private savings which are the lifeblood of a healthy economy. Second, low interest rates are effected by the Fed (or central bank) growing the supply of money at a faster rate than output (GDP). But that causes inflation after a lag of one to two years, forcing the Fed to contract the supply of money and destabilize growth. Third, cheap debt and high inflation (with negative real interest rates) encourage malinvestment in speculative assets that are expected to grow in price without necessarily growing output. The net result is that productive investment is crowded out by both malinvestment (speculation) and government deficits, harming long-term growth.
There is also a fourth, far more insidious factor, that operates with much greater lags. Home prices tend to grow at a much faster rate than incomes during times of low interest rates, reducing access to homes by younger workers entering the workforce. New household formation slows and so does the birth rate, undermining long-term demographics. This can be remedied to some extent by skilled immigration but often migrants are unskilled and face both language and cultural challenges that lead to poor assimilation and a two-tier economy.
In summary, what is needed is a growing, skilled workforce with rising productivity from healthy private investment. Private investment requires stable growth — to facilitate reliable projections rather than unstable boom-bust cycles — and sufficient funding from private saving. Government deficits need to be kept low and real interest rates reasonably high (say 3%) to ensure low inflation and encourage efficient allocation of capital (to productive private investment).
In the Wilderness
We are a long way from the above ideal.
The chart below shows the decline in 10-year average real GDP growth, since 1960, and rising debt relative to nominal GDP.

Growth is slowing due to poor demographics, rising government deficits, and malinvestment from negative real interest rates. Geopolitical tensions and the need to secure supply chains and sources of energy mean that government spending is likely to exceed tax revenues by a wide margin for the foreseeable future.
Ballooning government debt is likely to crowd out private investment, ensuring low future growth. The chart below shows CBO projections of debt-to-GDP for the next thirty years.
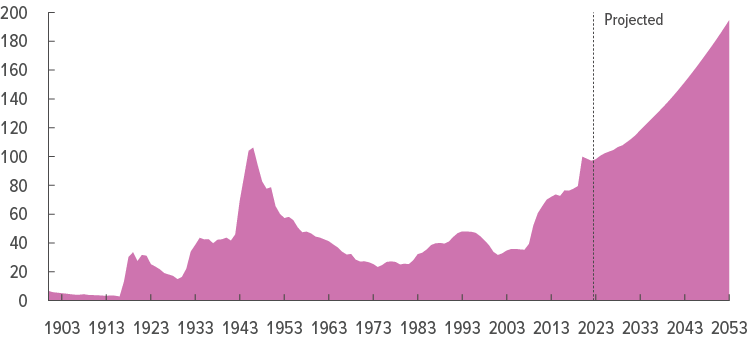
The Fed will likely have no choice but to suppress long-term interest rates in order to assist government in servicing the massive interest burden on its debt. That is likely to lead to high inflation, negative real interest rates, malinvestment in speculative assets, low growth, and rising instability (Hyman Minsky).
Conclusion
We are likely to face a decade of stagflation, with low growth, high inflation and unstable financial markets.
Hopefully, inflation will boost nominal GDP relative to government debt, increasing serviceability, over time. That would provide an opportunity to reduce fiscal deficits and establish healthy monetary policy.
In the meantime, don’t fight the Fed. When interest rates are low and inflation is high, invest in real assets. Look for value — with stable income streams which can withstand tempestuous cycles — rather than speculative growth.
Acknowledgements
Professor Percy Allan, University of Technology Sydney: Looking Beyond 2024
Save 50% on an Annual Subscription.